Customizing Label using LabelStyle
In the full tutorial…
- Built-in styles
- Basic styling
- Hovering labels
- Challenges
Subscribe to Hacking with Swift+ today
Hacking with Swift+ delivers high-quality tutorials for subscribers, with each tutorial coming as a 4K Ultra HD video and in text form so you can read or watch – whatever works best for you.
So, you can get this full video and article as well as all other subscriber-only tutorials and all future tutorials – all by subscribing to Hacking with Swift+ today.
Membership includes…
✅
All HWS+ tutorials as both text and 4K video
✅
Downloadable projects and learning challenges
✅
Our massive Ultimate Portfolio App series
✅
Access to my monthly app building livestreams
✅
Free gifts for every year of your subscription
✅
An ad-free experience everywhere on the site
✅
Video solutions for the 100 Days of SwiftUI
✅
A 20% discount on all my books year-round
✅
Access to an exclusive forum for subscribers
✅
Videos from Hacking with Swift Live
More from Hacking with Swift+
CUSTOM SWIFTUI COMPONENTS
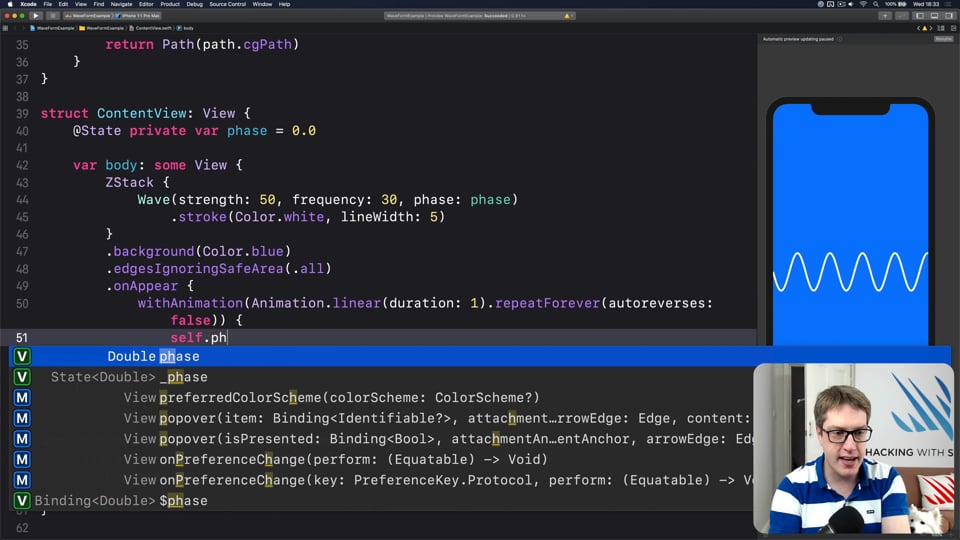
FREE: Creating a WaveView to draw smooth waveforms
In this article I’m going to walk you through building a WaveView with SwiftUI, allowing us to create beautiful waveform-like effects to bring your user interface to life.
HIGH-PERFORMANCE APPS
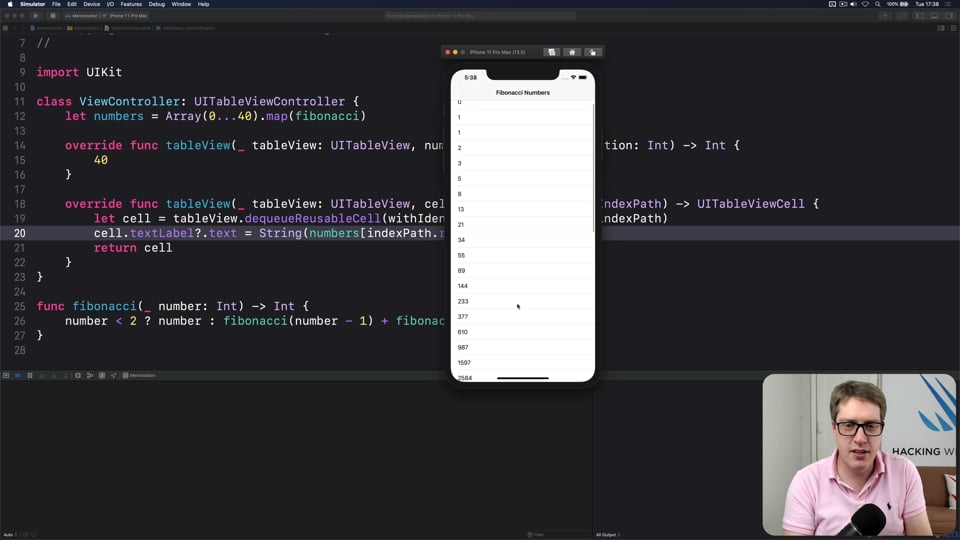
FREE: Using memoization to speed up slow functions
In this article you’ll learn how memoization can dramatically boost the performance of slow functions, and how easy Swift makes it thanks to its generics and closures.
SWIFTUI SPECIAL EFFECTS
FREE: Shadows and glows
SwiftUI gives us a modifier to make simple shadows, but if you want something more advanced such as inner shadows or glows, you need to do extra work. In this article I’ll show you how to get both those effects and more in a customizable, flexible way.
NETWORKING
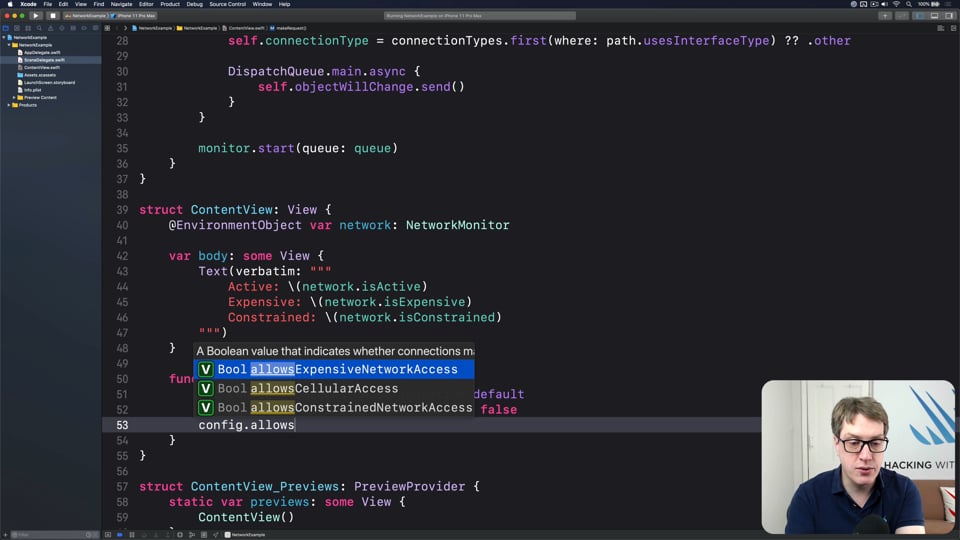
FREE: User-friendly network access
Anyone can write Swift code to fetch network data, but much harder is knowing how to write code to do it respectfully. In this article we’ll look at building a considerate network stack, taking into account the user’s connection, preferences, and more.
FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING
FREE: Transforming data with map()
In this article we’re going to look at the map() function, which transforms one thing into another thing. Along the way we’ll also be exploring some core concepts of functional programming, so if you read no other articles in this course at least read this one!
INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
FREE: Interview questions: Introduction
Getting ready for a job interview is tough work, so I’ve prepared a whole bunch of common questions and answers to help give you a jump start. But before you get into them, let me explain the plan in more detail…
ULTIMATE PORTFOLIO APP
FREE: Ultimate Portfolio App: Introduction
UPDATED: While I’m sure you’re keen to get started programming immediately, please give me a few minutes to outline the goals of this course and explain why it’s different from other courses I’ve written.
INTERMEDIATE SWIFTUI
FREE: Creating a custom property wrapper using DynamicProperty
It’s not hard to make a basic property wrapper, but if you want one that automatically updates the body property like @State you need to do some extra work. In this article I’ll show you exactly how it’s done, as we build a property wrapper capable of reading and writing documents from our app’s container.
DATA STRUCTURES
FREE: Trees
Trees are an extraordinarily simple, extraordinarily useful data type, and in this article we’ll make a complete tree data type using Swift in just a few minutes. But rather than just stop there, we’re going to do something quite beautiful that I hope will blow your mind while teaching you something useful.
INTERMEDIATE SWIFT
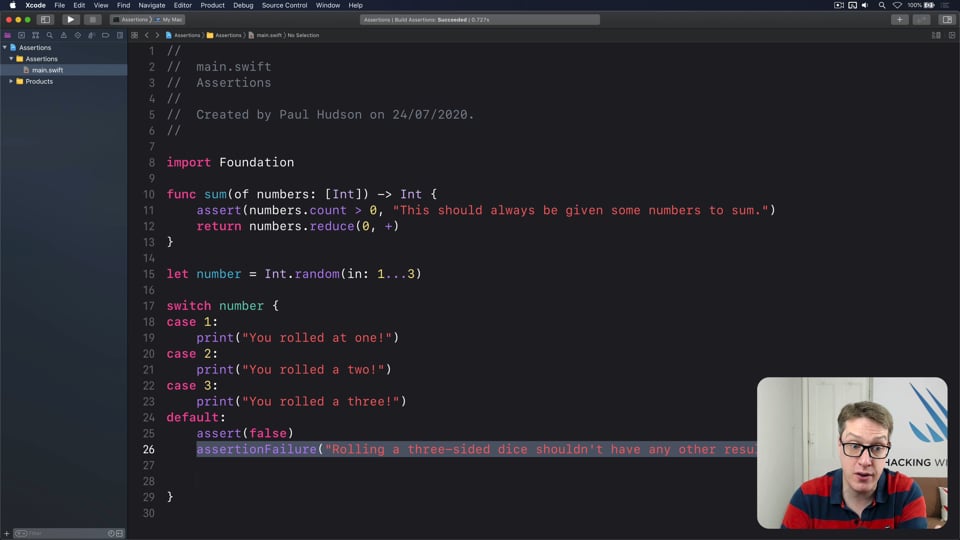
FREE: Understanding assertions
Assertions allow us to have Swift silently check the state of our program at runtime, but if you want to get them right you need to understand some intricacies. In this article I’ll walk you through the five ways we can make assertions in Swift, and provide clear advice on which to use and when.
ADVANCED SWIFT
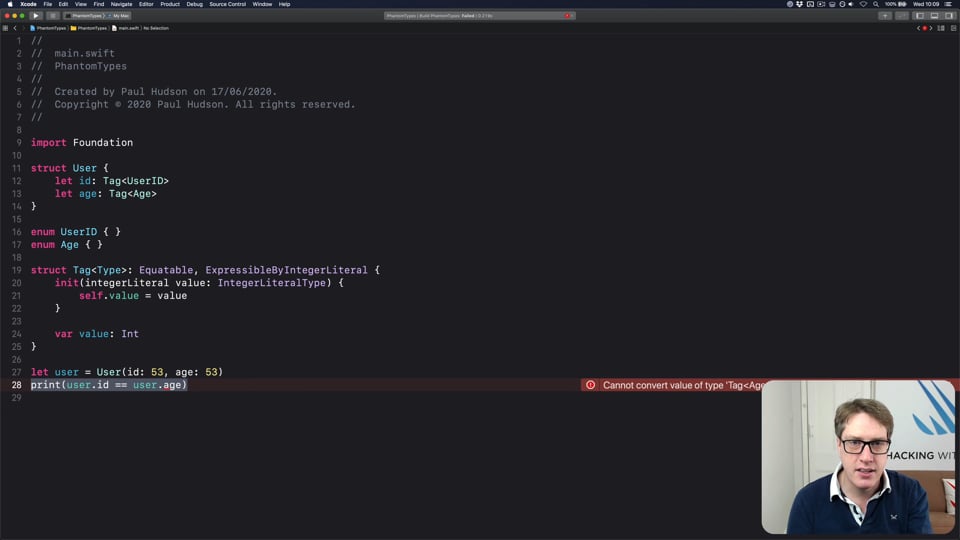
FREE: How to use phantom types in Swift
Phantom types are a powerful way to give the Swift compiler extra information about our code so that it can stop us from making mistakes. In this article I’m going to explain how they work and why you’d want them, as well as providing lots of hands-on examples you can try.
INTERMEDIATE SWIFT
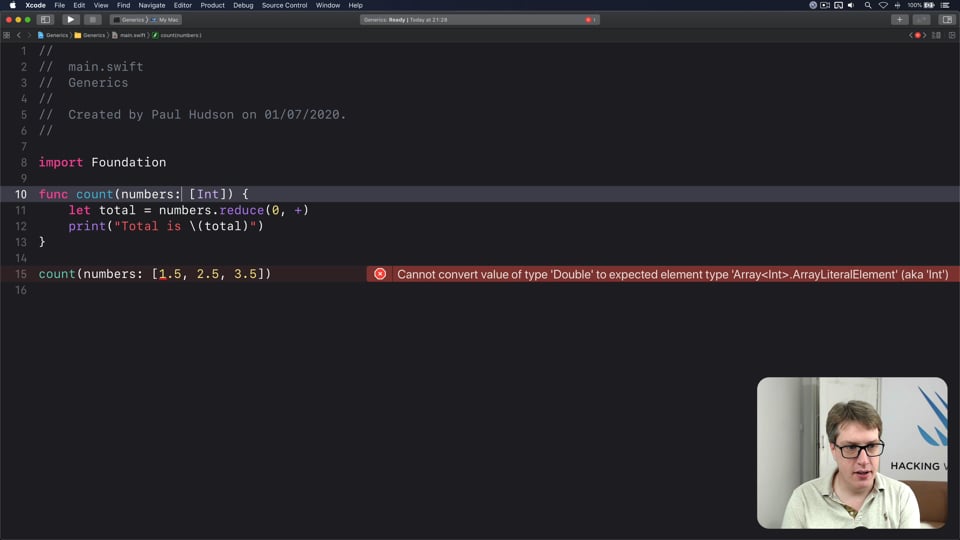
FREE: Understanding generics – part 1
Generics are one of the most powerful features of Swift, allowing us to write code once and reuse it in many ways. In this article we’ll explore how they work, why adding constraints actually helps us write more code, and how generics help solve one of the biggest problems in Swift.
FUNCTIONAL PROGRAMMING
FREE: Functional programming in Swift: Introduction
Before you dive in to the first article in this course, I want to give you a brief overview of our goals, how the content is structured, as well as a rough idea of what you can expect to find.
ADVANCED SWIFT
FREE: Making the most of optionals
Swift’s optionals are implemented as simple enums, with just a little compiler magic sprinkled around as syntactic sugar. However, they do much more than people realize, and in this article I’m going to demonstrate some of their power features that can really help you write better code – and blow your mind along the way.
SOLUTIONS
Core Data
This challenge asks you to adjust FilteredList in three ways: make it accept a string predicate, make it accept an enum predicate, then make it accept an array of sort descriptors for the managed object it uses. Let’s tackle it now…
EVENTS
Performance: the art of doing as little as possible
If you ever wondered why we write func and var rather than function and variable, it’s simple: programmers love being lazy! In this article we’re going to look at a handful of ways to make your projects faster by doing as little work as possible, just the way I like it…
REMAKING APPS
Remaking the iOS lock screen
In this article we’re going to look at how easy it is to rebuild the iOS lock screen. Yes, this isn’t hard, but along the way I think you’ll pick up a few cool SwiftUI tricks, including better date formatting, haptic buttons, and more.
ULTIMATE PORTFOLIO APP
First steps in UI
UPDATED: Now that we have our basic data model configured and coded, we can put it to use by building a simple user interface to help make sure our data is in place and working correctly.
SOLUTIONS
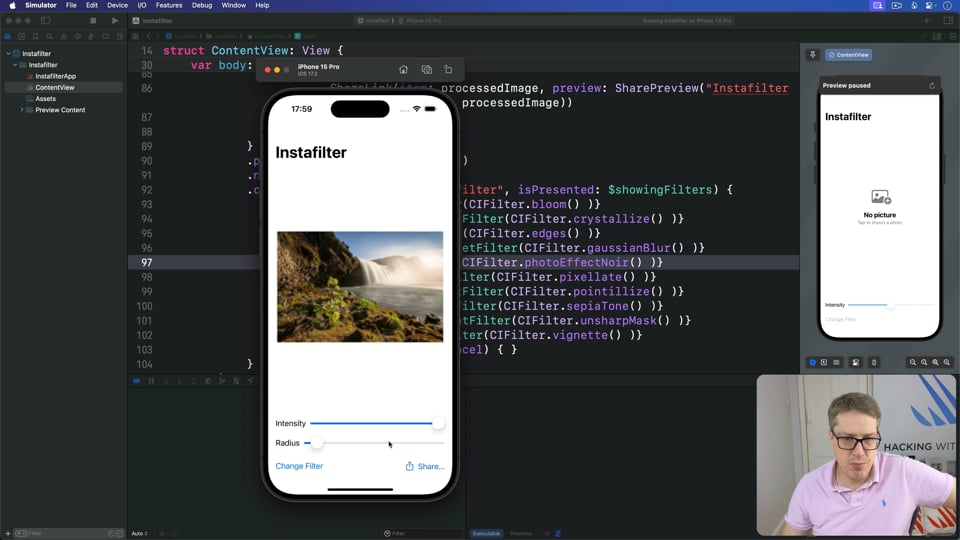
Instafilter
This challenge asks you to disable options when they don't make sense, add more sliders to control effects, and add three extra filters of your choice. Let’s tackle it now…
ULTIMATE PORTFOLIO APP
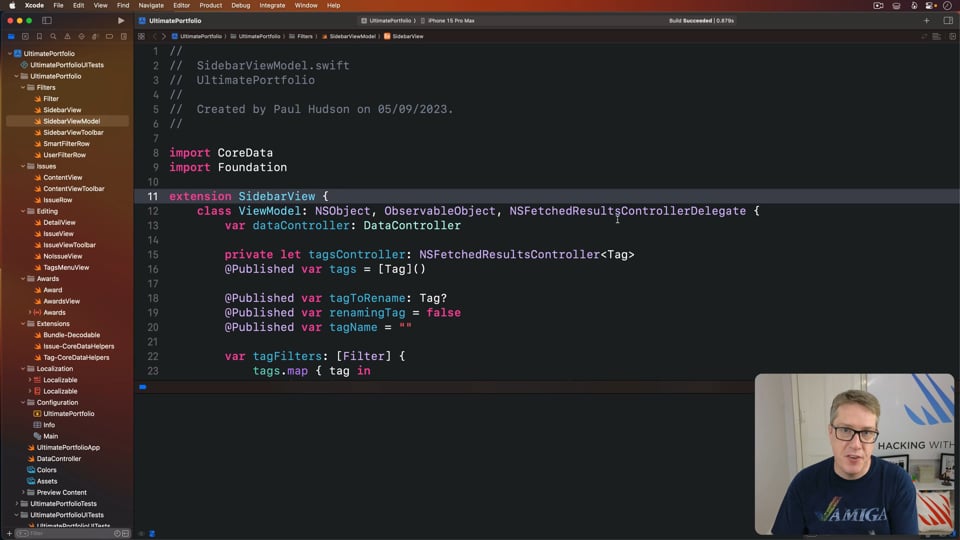
Bringing MVVM into our SwiftUI project, part 2
UPDATED: In this article we’re going to continue with our move towards MVVM, this time converting another two views that work well, but also looking at code that works less well so you can get a better idea of how SwiftUI and MVVM really fit together.